Continuous condition monitoring of fresh sludge and drainage pumps in the waste water industry
Waste water treatment plant Kressbronn
At the waste water treatment plant Kressbronn, numerous pumps with various characteristics are used to convey liquid media through the various areas of the waste water treatment plant. Unplanned downtime can have severe repercussions, potentially disrupting the entire municipal waste water disposal system or even causing a complete halt to its operations.
In the case of liquid pumps, bubbles can form if the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet side is too high: Resulting in cavitation. The tiny bubbles filled with vapour collapse suddenly due to the high pressure. This sudden collapse creates shock waves that repeatedly erode the pump element and the pump housing from the inside. If the damage becomes too great, the pump can no longer work properly. In the worst case, expensive repairs or even the replacement of the pump may become necessary.
The starting position
The fresh sludge and drainage pumps at the waste water treatment plant were not monitored continuously. The detection of pump bearing damage or potential cavitation was solely reliant on changes in operational noises. In the worst-case scenario, this could have resulted in unanticipated shutdown, significantly impacting the functionality of the waste water treatment plant and necessitating unplanned repairs.
Goal of the project
- Introduction of continuous recording and visualisation of the effective vibration values of the pump bearings in both axial and radial direction.
- Continuous recording and visualisation of the vibration values and temperatures of the pump motors.
- Monitoring and visualisation of the pumps for cavitation.
- Integration of an operating hours counter for cavitation cases within moneo to facilitate the detection of prolonged pump cavitation episodes.
- Avoidance of unplanned downtime.
- Alarm in case of limit threshold violations and cavitation.
Implementation
All the pump bearings and pump motors at the waste water treatment plant are equipped with vibration sensors and monitored. In addition, temperature sensors are installed on the motors to detect damage to the winding and to be able to avoid any resulting overheating in good time.
To reliably detect cavitation, the VSE150specifically monitors the frequencies that typically occur at pumps. The VSE150 is also responsible for configuring the thresholds, triggering alarms in case of threshold violations and analysing whether the respective pump is currently experiencing cavitation.
All the sensor values and alarms are recorded and displayed in moneo. Within moneo, a counter was set up for each pump, precisely calculating the duration of the pump’s cavitation state.
Success
Ensuring smooth operation at the waste water treatment plant
A comprehensive pump monitoring system was implemented, covering the critical areas of pump bearings and pump motors in the public infrastructure. Thanks to the diligent monitoring of thresholds, incipient bearing damage, pump contamination, cavitation, dry running, winding problems and motor contamination can now be promptly identified and addressed in a timely manner.
System structure
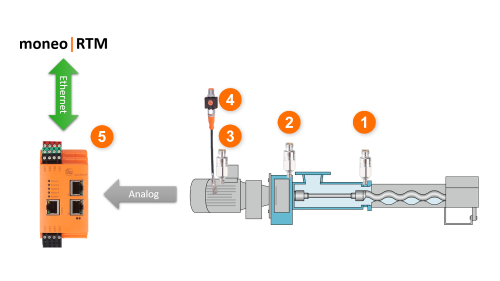
- Vibration sensor pump bearing NDE VSA001
- Vibration sensor pump bearing DE VSA001
- Vibration sensor motor bearing VSA001
- Temperature sensor motor TP3232 + TS2229
- Diagnostic electronics for vibration sensors VSE150


Our customer
The municipalities of Kressbronn a. B. and Langenargen jointly operate a waste water treatment plant in Eichert. Waste water is treated in four stages at the waste water treatment plant: Mechanically, biologically, chemically and with powdered activated carbon. The fourth treatment stage is particularly important as it filters trace elements (e.g. drug residues) out of the waste water. After the waste water has passed through all four treatment stages, it is finally discharged back into Lake Constance.
Dashboard
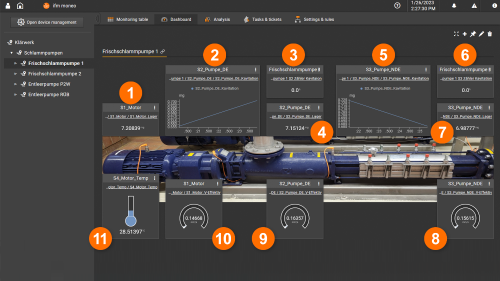
Fresh sludge pump 1
- Vibration motor bearing [mg]
- Cavitation recognition pump DE [mg]
- Time counter cavitation DE [h]
- Vibration pump bearing DE [mg]
- Cavitation recognition pump NDE
- Time counter cavitation NDE [h]
- Vibration pump bearing NDE [mg]
- V-effective pump bearing NDE [mm/s]
- V-effective pump bearing DE [mm/s]
- V-effective motor bearing [mm/s]
- Motor temperature [C°]
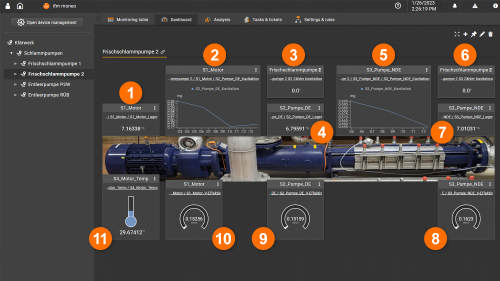
Fresh sludge pump 2
- Vibration motor bearing [mg]
- Cavitation recognition pump DE [mg]
- Time counter cavitation DE [h]
- Vibration pump bearing DE [mg]
- Cavitation recognition pump NDE
- Time counter cavitation NDE [h]
- Vibration pump bearing NDE [mg]
- V-effective pump bearing NDE [mm/s]
- V-effective pump bearing DE [mm/s]
- V-effective motor bearing [mm/s]
- Motor temperature [C°]

Drainage pump stormwater overflow tank
- Motor temperature [C°]
- Vibration motor bearing DE [mg]
- Vibration motor bearing NDE [mg]
- a Peak pump radial [mg]
- a Peak pump axial [mg]
- Cavitation recognition pump [mg]
- Time counter cavitation [h]
- V-effective pump [mm/s]
- V-effective motor [mm/s]
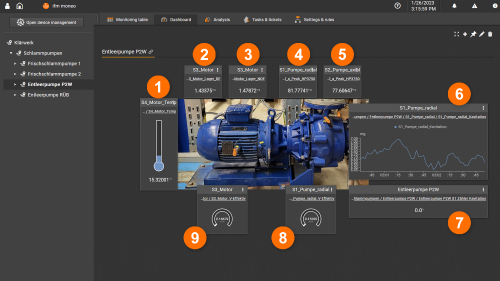
Drainage pump P2W (process water)
- Motor temperature [C°]
- Vibration motor bearing DE [mg]
- Vibration motor bearing NDE [mg]
- a Peak pump radial [mg]
- a Peak pump axial [mg]
- Cavitation recognition pump [mg]
- Time counter cavitation [h]
- V-effective pump [mm/s]
- V-effective motor [mm/s]